8304. Fun function
Find the value of the function
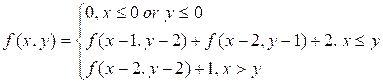
Input. Two integers x, y (0 ≤ x, y ≤ 50).
Output. Print the value of the function f(x, y).
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
2 3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
34 12 |
6 |
SOLUTION
recursion
Algorithm analysis
Implement a recursive
function with memoization.
Algorithm
implementation
Declare a two-dimensional
array to store the function values: dp[x][y] = f(x, y).
long long
dp[51][51];
Implement the recursive
function f with memoization.
long long
f(int x, int y)
{
if (x <= 0 || y <= 0) return
0;
if (dp[x][y] != -1) return
dp[x][y];
if (x <= y) return
dp[x][y] = f(x - 1,y - 2) + f(x - 2,y - 1) + 2;
return dp[x][y] = f(x - 2,y - 2) + 1;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
Initialize
the cells of the dp array with the
value -1.
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
Call the
function f(x, y) and print its value.
printf("%lld\n",f(x,y));
Python implementation
Implement the recursive
function f with memoization.
def f(x, y):
if x <= 0 or y <= 0: return 0
if dp[x][y] != -1: return dp[x][y]
if x <= y:
dp[x][y] = f(x - 1, y - 2) + f(x - 2, y - 1) + 2
else:
dp[x][y] = f(x - 2, y - 2) + 1
return dp[x][y]
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
x, y = map(int, input().split())
Declare a two-dimensional
list to store the function values: dp[x][y]
= f(x, y). Initialize
the cells of the list with the value -1.
dp = [[-1] * 51 for _ in range(51)]
Call the
function f(x, y) and print its value.
print(f(x, y))